The vast oceans have long been highways for maritime trade, but this constant ship traffic creates an invisible threat beneath the waves. For marine mammals like whales that rely on sound for communication, navigation, and hunting, the growing cacophony of vessel noise has become an existential crisis. Now, an innovative acoustic monitoring system is creating quiet zones to protect these sensitive giants of the deep.
The Silent Crisis Beneath the Waves
Whales inhabit a world of sound. In the ocean's dark depths where light penetrates poorly, these marine mammals evolved over millions of years to depend on acoustic signals. Their sophisticated sonar systems can detect prey miles away, while complex songs carry across entire ocean basins to potential mates. But this sonic landscape is being drowned out by an ever-increasing barrage of ship noise.
Large vessels produce low-frequency sounds that travel hundreds of miles underwater, overlapping exactly with the frequencies whales use. Studies show some species must now shout to be heard, increasing their stress levels and reducing communication ranges by up to 90%. For the endangered North Atlantic right whale with fewer than 350 individuals remaining, this acoustic smog may prove the final push toward extinction.
Smart Buoys Create Acoustic Safe Havens
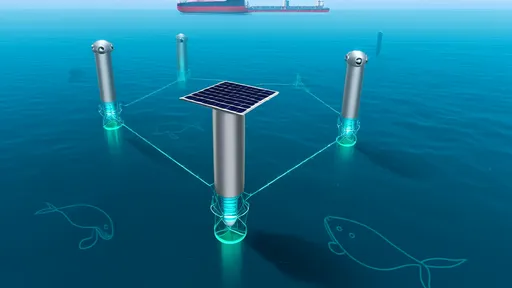
The solution now being deployed off busy coastal areas resembles a high-tech "firewall" against noise pollution. Networks of intelligent buoys equipped with hydrophones constantly monitor underwater soundscapes in real time. When whales are detected through their distinctive calls, the system automatically alerts nearby ships to slow down or reroute, creating temporary quiet zones.
These buoy networks use machine learning algorithms that can distinguish between over 20 whale species by their vocalizations. The floating sentinels communicate via satellite, feeding data to both maritime authorities and commercial shipping companies. Early implementations off the U.S. East Coast and Canada's Bay of Fundy have demonstrated remarkable success, reducing dangerous ship strikes while allowing whale populations to reestablish critical behaviors.
How the System Creates Quiet
When the acoustic buoys detect whale activity in shipping lanes, they trigger a multi-layered response. First, automated alerts go out to all vessels within a 50-nautical-mile radius through existing maritime communication systems. Large ships receive specific requests to reduce speed below 10 knots, which dramatically lowers their noise footprint.
For areas with persistent whale presence, the system can recommend temporary traffic separation schemes - essentially underwater detours that keep loud vessels away from sensitive habitats. The buoys' real-time monitoring allows these measures to remain in place only as long as needed, minimizing disruption to shipping schedules.
Technological Symphony for Marine Conservation
Each smart buoy represents a marvel of marine engineering. Solar panels and wave-powered generators provide continuous energy, while multiple hydrophones at different depths create a three-dimensional picture of acoustic activity. Advanced signal processing filters out natural background noise like waves and rain to focus on biologically significant sounds.
The system's artificial intelligence component grows more sophisticated with each passing season. By analyzing years of acoustic data across different regions, it can now predict seasonal whale migrations and preemptively alert ships when populations are likely to traverse busy shipping channels. This predictive capability marks a major leap from reactive to proactive whale protection.
Human and Economic Benefits
While primarily designed to protect marine life, the acoustic monitoring network delivers unexpected advantages for human stakeholders. Shipping companies benefit from reduced risks of costly collisions and damage to vessels. Port authorities gain tools to optimize traffic flow while demonstrating environmental responsibility.
Perhaps most significantly, the system provides scientists with unprecedented datasets about whale behavior, population dynamics, and responses to human activity. This treasure trove of acoustic ecology data helps refine conservation strategies and may guide future marine spatial planning initiatives.
Challenges and Future Expansion
Despite its successes, the technology faces limitations. Maintaining equipment in harsh marine environments requires regular servicing, and the high initial costs have slowed widespread adoption. Some shipping operators initially resisted speed reduction requests until legal frameworks made participation mandatory in certain regions.
Looking ahead, researchers aim to expand buoy networks along major migration corridors worldwide. Smaller, more affordable versions could protect coastal dolphin populations, while deeper-water variants might safeguard beaked whales in offshore habitats. Integration with emerging "smart shipping" technologies could eventually create fully automated vessel speed adjustments when whales are detected nearby.
The quieting of our oceans represents one of conservation's greatest challenges of the 21st century. As this innovative acoustic monitoring system demonstrates, technology coupled with thoughtful policy can help restore balance to marine ecosystems. By giving whales back their voice, we preserve not just endangered species but the very symphony of life in our planet's blue heart.

By /Aug 7, 2025

By /Aug 7, 2025

By /Aug 7, 2025

By /Aug 7, 2025
By /Aug 7, 2025

By /Aug 7, 2025
By /Aug 7, 2025

By /Aug 7, 2025

By /Aug 7, 2025

By /Aug 7, 2025

By /Aug 7, 2025

By /Aug 7, 2025

By /Aug 7, 2025
By /Aug 7, 2025

By /Aug 7, 2025

By /Aug 7, 2025

By /Aug 7, 2025

By /Aug 7, 2025

By /Aug 7, 2025

By /Aug 7, 2025